Application
Integration Architecture – a definition
AIA = The foundation for Adaptive Business Solutions product offerings. AIA includes a service-oriented application architecture and standards-based enterprise business objects and services. Each component includes development and extension methodologies, implementation best practices, and infrastructure extensions required to support the delivery of Oracle’s Process Integration Packs as prepackaged, upgradeable, and supported application product offerings.
Why EBO …
Enterprise Business Object (EBO)
AIA = The foundation for Adaptive Business Solutions product offerings. AIA includes a service-oriented application architecture and standards-based enterprise business objects and services. Each component includes development and extension methodologies, implementation best practices, and infrastructure extensions required to support the delivery of Oracle’s Process Integration Packs as prepackaged, upgradeable, and supported application product offerings.
Application Integration Architecture Components
•Industry Reference Models
-Documented
best-practice processes
-Pre-defined
standards based enterprise business objects and services
-
•Process Integration Packs
-Pre-built
integrated orchestration flows – Example: Order to Cash (Siebel to E-Business
Suite)
-Extensible
enterprise business objects and services associated with Oracle Applications
-Methodology
for building and extending Process Integration Packs and Industry Reference
Models
-Combination
of Oracle Fusion Middleware, common object /service definitions, best practice
designs, extension methodologies and life cycle management tool add-ons
AIA Terminology:-
-Enterprise Business Service (EBS)
•These are application-agnostic web services that are used by
calling applications to interface with different applications. This helps the
cross-application processes to be participating-application unaware. The EBM
containing the canonical object is the payload of the enterprise service and
contains business-specific messages.
-Enterprise Business Object (EBO)
•A standard business data object definition used in the
canonical data model. Enterprise business objects contain components that
satisfy the requirements of business objects from participating application
data models.
-Enterprise Business Message (EBM)
•The EBM is the payload that is paired to an EBS. The response
returned by the EBS will also be an EBM.
-Enterprise Business Flow (EBF)
•A cross-functional BPEL flow is used to coordinate the flow
of a single EBS operation that is complex, potentially long-lived, and spans
multiple services. These flows only interact with EBSs to keep them agnostic of
participating applications.
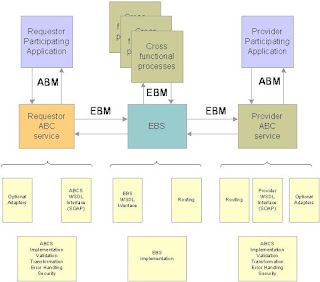
-Application Business Connector Service (ABC Service)
The name for APIs developed to
transform application business objects into enterprise business objects, and
vice versa. Components of this service include the ABC implementation service
and the ABC interface service.
“Order to Fulfillment”
What is an EBO…
1). Common Object definition of
business concepts such as a customer, a sales order, a payment etc
2). Defined using inputs from multiple
applications and content standards
3). Precise definition of each business
component and attribute by adoption of standards for both content as well as
naming and design
4) . Designed for extensibility
• Standard Services require standard payloads to be truly
application independent
-EBOs are standardized representations of
business objects that will serve as the payload (input or output) for standard
services
-EBOs are based on standards published by
international standards organizations
•UN/CEFACT Core Components Technical Specification (CCTS)
•Open Applications Group Integration
Specification (OAGIS)
ØEliminates Point to Point Duplication-
P2P works when connecting two systems but requires a complete re-implementation when you introduce a second service provider / requester
ØSupports One to Many Model -
For Integrations that map one service request to many service providers (or vice versa), EBOs allow re-use of initial implementation and reduces overall number of transformation maps to generate
ØHot Pluggable-
Common Objects abstracts application service providers from service requesters and centralizes routing and mediation which allows any application to plug into the integrated process flow
ØStandards Based Content to drive Interoperability-
ØEliminates Point to Point Duplication-
P2P works when connecting two systems but requires a complete re-implementation when you introduce a second service provider / requester
ØSupports One to Many Model -
For Integrations that map one service request to many service providers (or vice versa), EBOs allow re-use of initial implementation and reduces overall number of transformation maps to generate
ØHot Pluggable-
Common Objects abstracts application service providers from service requesters and centralizes routing and mediation which allows any application to plug into the integrated process flow
ØStandards Based Content to drive Interoperability-
EBOs are based on OAG content and rationalized against Oracle Applications for
the most common A2A and B2B integration use cases
Enterprise Business Object (EBO)
Logical
Model Representation
•UML Class Diagram
•ISO 11179 Compliant
•CCTS Support
Core
Common Model
•Common Attribute Validation
•Common Enterprise Services
Leverage
OAG as base
•Rationalized against Oracle Apps
•Reconciled against Fusion Apps
Versioning
Support – Backward and Forward Compatibility
What is Enterprise Business Service?
Standardized Service definitions across applications
Enterprise
Business Services:-What is Enterprise Business Service?
Standardized Service definitions across applications
•Standard service definitions that are implemented by all
Oracle applications
-A single service supporting multiple
operations – e.g. SalesOrder Service may support Create, Cancel, Update Operations
-Each operation will use application
independent data structures as standard input and/ or output
-Multiple applications may provide the same
service e.g. E-Business Suite (EbizS), Siebel, Enterprise and E1 can support Create Sales Order
-Objective is to be able to switch the
service provider without affecting the service e.g. switch from EbizS
or E1 to Fusion (or any other partner applications that provide the same
service
Service
Types:-
Enterprise Business Flow – An Example
Application Business Connector Service:-
•Entity Services
-Each
of the Enterprise Business Object will have a service
-Common
Enterprise Business Services:
•Item
•Invoice
•SalesOrder
•
-Entity
Services will have following types of operations
•CRUD
Operations
•Custom
Actions
•Bulk
Processing
•
•Process Services
-Business
Processes will have their own services
•SalesOrderOrchestration
PriceDropOrchestrationEnterprise Business Flow – An Example
Application Business Connector Service:-
•Facilitates the exposing of core business
transactions as well as data access as web services
•Serves as a glue to integrate applications with Enterprise
business services
•Allows for participating applications to
become service providers as well as service consumers without disruption to
code
•Allows for applications having non standard
connectivity to expose their functionality as services
AIA
Integration Scenario – End-to-End Flow






This is very useful for Oracle AIA Learns ...............
ReplyDeleteThanq For The Info....
ReplyDelete